On May 7th, the currency was hacked and more than 7,000 bitcoins were missing.
The currency explained that the hacker used phishing, viruses and other means of attack, obtained a large number of registered users’ API keys, Google verified 2FA code and other information, and finally completed the withdrawal operation. The security company also analyzed that the incident is likely to be caused by long-term APT penetration of the intranet, which is the result of long-term hacking.

On May 26, the easy-to-use car released a notice saying that its server was attacked, and the attacker demanded huge amounts of bitcoin, which made it easy to encrypt the core data and the server was down.
As the value of cryptocurrency becomes more and more significant, hackers who have targeted large players in the past have begun to turn their attention to ordinary players. In the face of skilled and sophisticated hackers, ordinary people have no power to look at assets. disappear”.
In fact, the hacker’s approach is not very clever. Sometimes, relying on a blank SIM card or an alarmist email, it can be easily stolen or scammed by the cryptocurrency that you have painstakingly stored.
This kind of “gravity and plunder” is still spreading. In recent years, the Lazarus Group, a hacker organization directly under the North Korean government that has been working with the world’s major banks and cryptocurrency exchanges, has begun to target. From the big to the individual, just stealing the expensive cryptocurrency assets of these people.
When will this cat and mouse game end?
SIM Swap Scam
“They ruined my life.”
A man from San Francisco collapsed. He had just punched the coin into his wallet the next second. The next second, the coin in the address was instantly zeroed. Soon he discovered that he was taken into a scam called “SIM Swap Scam” without knowing it.
The sudden display of “no service” by the mobile phone often indicates the opening of the scam.
Recently, a hacker named Daniel, who appeared in Trijo News, disclosed how he easily stole $500,000 in cryptocurrency in just one year. “I am only about 20 people, it is not particularly active.” Daniel said that he mainly used the “replace SIM card” method, eventually stealing other people’s cryptocurrency.
Once he is eyeing certain “prey,” he pretends to be a victim, calls the telecommunications company, tells the operator that there is a problem with his mobile number, and asks for the information to be transferred to the number he controls.
Although telecommunications companies have set up various risk control measures, “there are always ways to convince operators.” For example, when you are on the phone, you can pretend that you are working at Tele2 (a Swedish telecom company) and ask them to help. You can forward a number,” Daniel said.
In fact, Daniels are not simply intercepting the mobile phone number. Their ultimate goal is the secret key. “Many people will keep the cryptocurrency key on an e-mail or a networked computer.” This rigorous practice has given hackers Take the opportunity.
Once the phone number is locked, the hacker will go to the victim’s Gmail or Outlook account, enter the address and click Forgot Password, then select the verification code for the victim’s mobile phone number by voice (actually this is mainly to help the visually impaired In this way, it is easy to bypass the so-called two-factor authentication (2FA).

He said, “Many people don’t pay enough attention to this, which is a rare opportunity for us.” In this way, Daniel, who is not active, has stolen another $500,000 in cryptocurrencies in a year. .
In fact, it is not uncommon to use a SIM card to steal someone else’s cryptocurrency case.

Last year, a 21-year-old young man, Nicholas Truglia, led a team that attacked more than 40 people in a similar way and stole tens of millions of dollars worth of cryptocurrency.
Fortunately, the team members were eventually captured, and the victim, Michael Terpin, received huge compensation for filing a civil lawsuit in court; another victim, Robert Ross, A website called “Stop SIM Card Crime” was set up to disclose such crimes.
Similar incidents did not stop, and even the senior code farmers did not escape.
On May 20th, Sean Coonce, director of cryptocurrency hosting company BitGo, was also hacked in a similar way, stealing more than $100,000 worth of bitcoin from his Coinbase account. Coonce called it “in his life.” “The most expensive lesson.”
When you watch porn, the hacker is staring at you.
Food color is also the instinct of human beings, but if it is used by hackers, it may also produce evil.
In the third episode of the third season of the American TV series “Black Mirror”, the boy Kenny was hacked because of the child pornography. In order to prevent such “violation” from being publicized, Kenny could only be threatened and completed. The hacking instructions for delivery, robbery, and even murder.

The same encounter with Kenny in the play, as well as the CEO with the glamorous identity, the uncle who derailed, and so on, all because the hackers mastered their “black materials”, and finally went on the road of no return with the same men.
In fact, such a thing does not only exist in film and television dramas, but also a similar story in real life, and all of this begins with an e-mail.
In July last year, Cornell University professor Emin Gün Sirer tweeted that his friend received an email saying that the process of watching pornography had been discovered and that a ransom must be paid to avoid video exposure. I have my own bitcoin address.
In this regard, Emin Gün Sirer speculated that the message was sent to everyone on the haviebeenpwnd list, he warned, “Be careful, don’t pay, don’t compromise.” Be careful out there, never pay, never negotiate. ).”
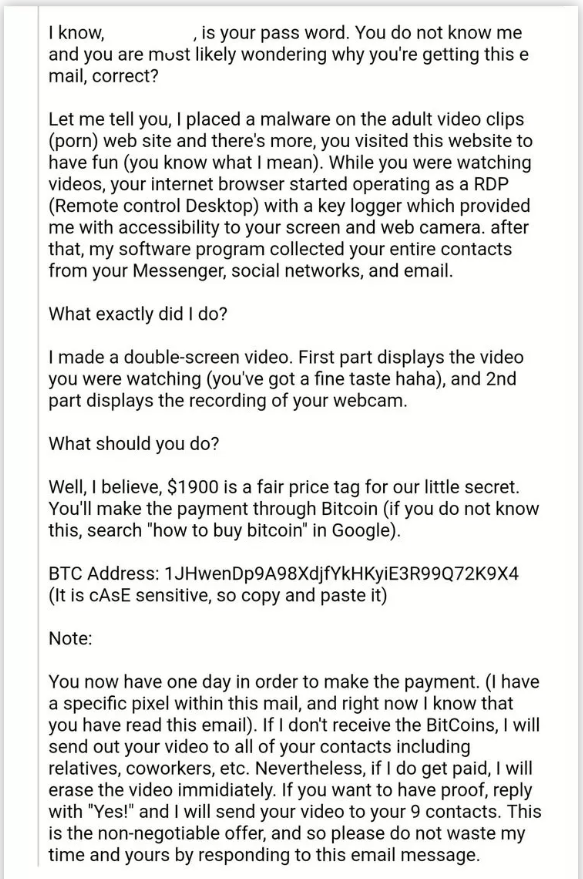
The hacker said in the mail that they had access to the recipient’s webcam and sensitive information, and there was evidence that they were viewing pornographic content on the Internet. If they did not pay the ransom (usually they need to pay cryptocurrencies for concealment), they would Information is sent to the recipient’s friends and family. If some people, like Kenny, succumb to the threat of hackers, they are likely to hit the ransom at the address left by the other party.
In fact, such an example is not uncommon.
Under the professor’s tweet, it was revealed that I received two emails with the same meaning. “The only difference is the amount of demand and the address of the cryptocurrency”. The first email asks for $1,200, and the second email asks for $2,900. .
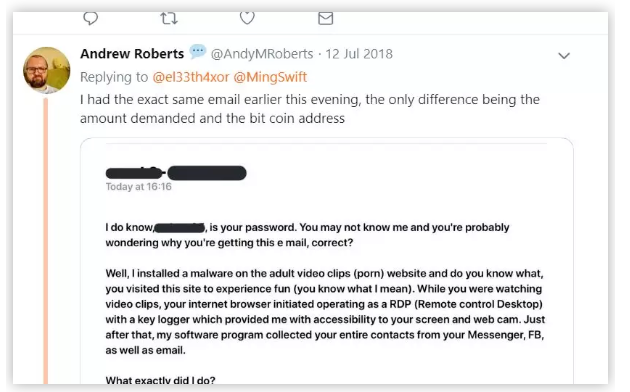
Since this type of encryption scam called “Sextortion” was exposed in 2017, it quickly became popular.
IBM security researchers say that in just one month, hundreds of emails written in English, French, Japanese, and Arabic were sent out, “If you don’t send Bitcoin to the specified address, you don’t ask for it.” The video will be sent to your friends and colleagues.”
The hacker used this reason and the situation of extortion was rampant.
Network security company Digital Shadows has published a data. According to incomplete statistics, since last July, sextortionists have used the scam to make about 332,000 US dollars. These hackers have targeted the shooting of nearly 90,000 people. The total number of messages posted was 792,000, and the total of more than 3,100 addresses of Bitcoin was deposited into the hacker’s 92 bitcoin wallets.
North Korean hacker
North Korean hackers have always been a hidden existence.
According to previous surveys, the targets of “care” by Korean hackers in the early years, including the central bank of Bangladesh, South Korea TV, Sony Pictures and other financial institutions/companies, they have superb technology and organized actions, and have made ATMs in dozens of countries. The machine has a problem of spitting money and has obtained a lot of “unjust money”.
With the rise of Bitcoin, the anonymity of the cryptocurrency itself began to be “favored” by North Korean hackers. According to data released by Russian network security company Group-IB, since 2016, North Korean national hacking organizations have cracked five cryptocurrency exchanges and stole 580 million US dollars of cryptocurrency, accounting for 64.7 of the total number of cryptocurrences stolen. %.
The prevention of financial institutions and cryptocurrency trading platforms has been continuously strengthened, and North Korean hackers have begun to turn their attention to ordinary people with weak security awareness.
“In the past, hackers attacked the exchange directly,” said Simon Choi, founder of the wiki warfare research firm IssueMakersLab. “But now they are directly attacking cryptocurrency users.”
Kwon Seok-chul, CEO of South Korean network security company Cuvepia, also publicly disclosed that since April last year, they have found traces of North Korean hackers in more than 30 cases of theft. “When cryptocurrencies are stolen by hackers, victims often complain. There is no door, only to give up.” He added that the number of cases that have not been discovered may exceed 100.
It is understood that North Korean hackers usually send emails with text files to the victim. Once the recipient opens the file, the malicious code inside will infect the computer and control the computer easily.
“Most of the victims have been relatively wealthy Koreans, such as company CEOs.” He revealed that the reason is that this group of people is worth more, “it can mobilize billions of cryptocurrencies by itself.”
There is nothing new under the sun. In the dark corners that are not known, hackers who use bitcoin for extortion still exist.
Recently, CipherTrace said in the “First Quarter of 2019 Cryptographic Money Anti-Money Laundering Report” that the cryptocurrency loss caused by hacking and fraud in the first quarter of this year was as high as 1.2 billion U.S. dollars, almost 1.7 billion U.S. dollars lost last year. 71%.
For ordinary people, only by strengthening self-security awareness and avoiding the disclosure of sensitive information such as cryptocurrency private keys, can they better protect themselves from hackers.